
Facilities and equipment
This section of the Novartis RLT Institute reviews the considerations in setting up the facilities and equipment required to provide radioligand therapy (RLT).
Key spaces
Hot lab
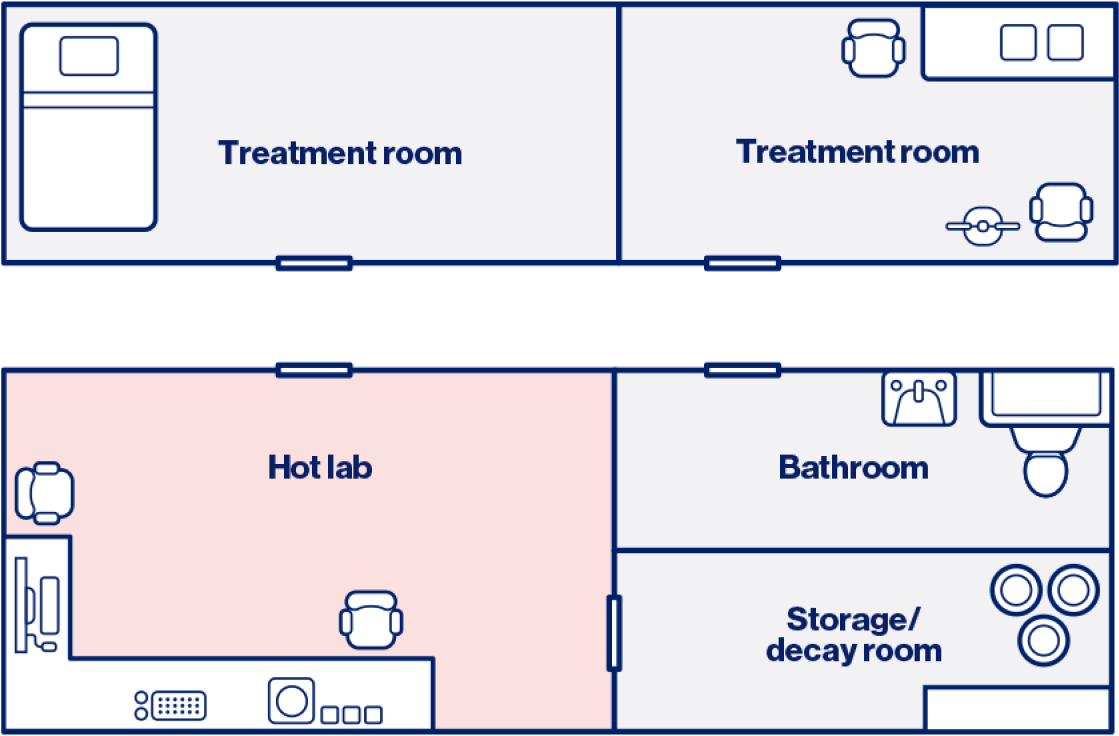
Diagram provided for illustrative purposes only; institutions should adhere to their internal guidance and are responsible for ensuring legal and regulatory compliance.
A hot lab is a secure, locked-door, controlled-access space designed for the safe preparation, handling, and storage of radioactive pharmaceuticals used in medical or research applications. The area must be clearly marked with radiation signage.1-3
The hot lab must be equipped with the appropriate facilities to handle radioactive material safely, including adequate space to fit packages, designated workspace for handling the product, shielding, contamination monitors, and tools for measurement.1-3
These considerations need to be accompanied by the appropriate documentation on how access will be controlled, and provisions for how the regulatory limit will be ensured.4
This facility operates under established safety protocols to manage radiation exposure, contamination risks, and waste disposal in compliance with safety and radiation protection standards from the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, ensuring protection for personnel and the environment.1
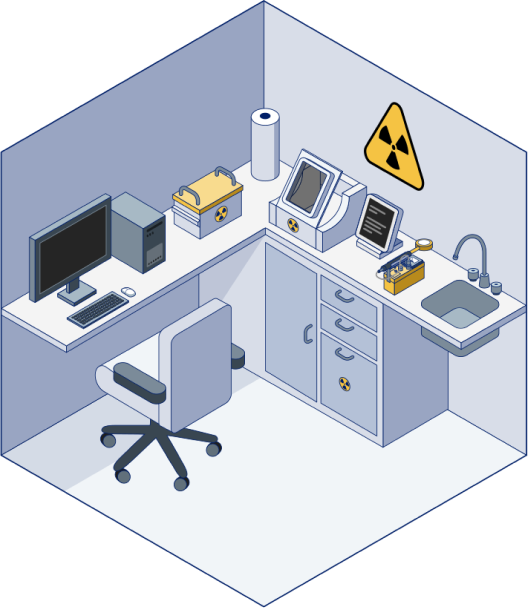

Key processes in this space
- Proper radioactive material (RAM) receiving procedures: Package check-in to ensure physical integrity of package and no contamination during transport5
- Checking in the dose: Labeling and documentation of materials; secure storage in a shielded container until use6-9
- Preparation of the dose: Confirming the exact activity of the dosage to be administered to the patient6
- Handling waste materials: Any RAM waste materials generated during processing or administration should be securely contained in a designated, shielded space safely for decay, storage, or disposal. This process must follow local or institutional guidelines.1,8
Facility flow
For each step in the facility flow, follow federal and/or local guidelines.

1. Receipt and logging
RLTs are delivered and logged upon arrival.10
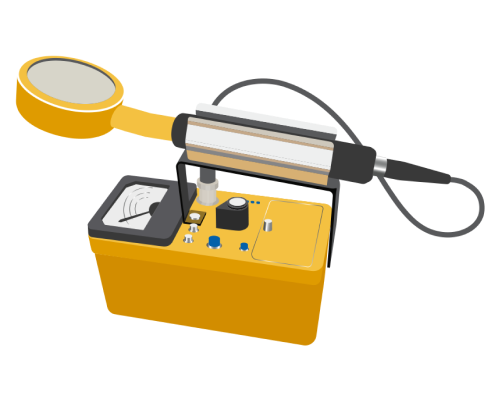
2. Inspection and verification
Materials are inspected for integrity and radiation levels are verified.10

3. Dose confirmation
The radiopharmaceutical dose is prepared using a dose calibrator to measure activity.10
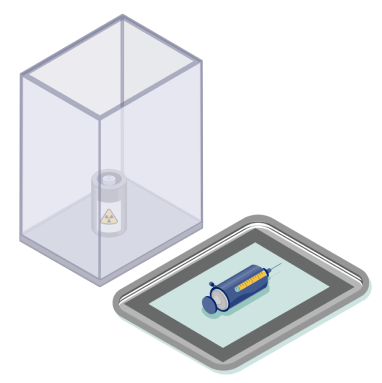
4. Shielded transport
Prepared doses are placed in shielded containers for safe transport to the treatment room. When in transport, RAM should always be kept in the shielded container and away from the body (and bystanders) to minimize exposure.1,14
Specific considerations
- Proper labeling is critical in any hot lab per federal, local, and institutional regulations. This keeps health care staff and patients safe while ensuring that processes are efficient.6,7,9
- The hot lab should be located away from high-traffic areas like waiting rooms, primary hallways, or elevators to minimize radiation exposure and prevent contamination. As a sterile environment for handling sensitive products, it must remain clean and free from external disruptions.1,14
