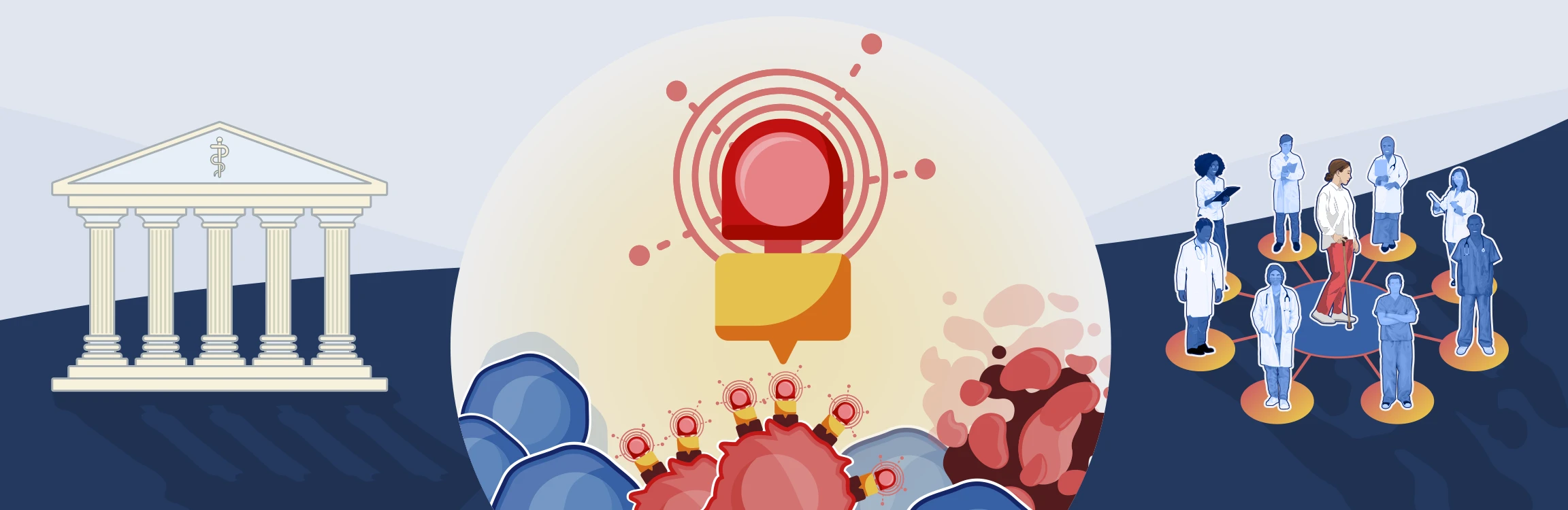

Foundations of theranostics
Radioligand therapy (RLT) and radioligand imaging (RLI) offer a novel, theranostic approach to targeting and treating certain types of cancer.1 This section of the Novartis RLT Institute is designed to help health care professionals (HCPs) understand the basic scientific foundations of RLT. By focusing on the science, we aim to demystify radiation and safety concerns and build confidence in offering patients this approach to precision medicine in cancer.
Radiation safety fundamentals
Safety equipment
Radiation detection equipment
There are many different types of equipment used to detect radiation, including2,3:

Dose calibrator
Measures the activity of RLI and RLT doses to ensure accurate and safe administration

Personal dosimeter
Monitors radiation exposure for staff, ensuring levels remain within safety limits

Survey meter
Detects ambient radiation and contamination on surfaces, equipment, or personnel
For ambient radiation and contamination surveying, the area is typically surveyed with a Geiger counter or scintillation survey meter. In the case of contamination, removable contamination can be detected and measured by conducting a wipe test of the surface, counted in an appropriate instrument, such as a liquid scintillation counter.4
Equipment for shielding and distance5-10

Syringe shield
Reduces radiation exposure to staff during dose preparation and administration

Type A radioactive shipping container
Safely transports radioactive materials, enabling containment and shielding

Glass vial and lead-shielded container
Protects staff and the environment by containing radioactive materials during shipping and handling

Acrylic beta shield
Blocks beta particles to protect staff during preparation and handling

L-block
A large shield providing protection from radiation while working with radioactive materials
Forceps
Allows safe handling of radioactive materials by increasing distance from the source
