Providing and administering RLT
This section of the Novartis RLT Institute is designed to help health care professionals (HCPs) understand radiation safety procedures for providing and administering radioligand therapies (RLTs) manufactured by Novartis. It is based on guidelines from regulatory agencies, including the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), the Department of Transportation (DOT), and the United States Pharmacopeia (USP). Topics include safe transport, administration, and postadministration protocols to prepare the patient and room for subsequent use.
Administering RLT
Administration methods
RLTs like PLUVICTO® (lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan) and LUTATHERA® (lutetium Lu 177 dotatate) can be administered using different techniques, with the method chosen based on patient safety, institutional guidelines, and product labels.1-3
Administration methods include:
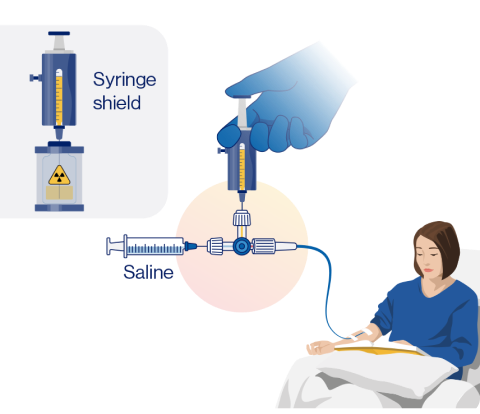
Syringe method
(+/- syringe pump)
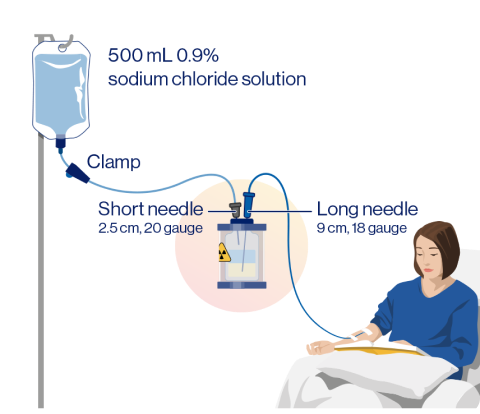
Gravity method
(+/- an infusion pump)
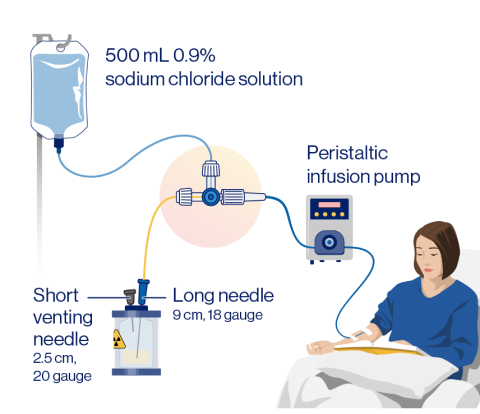
Vial with peristaltic infusion
pump method
- Each administration method has distinct advantages and limitations, and the selection should prioritize patient safety, align with institutional guidelines, and adhere to product labeling3
- The method of administration may vary with the type of RLT therapy being administered3
- Refer to the product-specific administration guides for detailed information on dosing, concomitant medications, treatment considerations, and patient monitoring3
Equipment by method of administration
Equipment needs will vary based on the selected method of administration. Maintaining a comprehensive inventory of all necessary equipment for each technique, along with backups to address potential contamination or situations where equipment in use may need to be temporarily removed from service, facilitates safe and smooth operations.3
| Equipment | Syringe method | Gravity method | Vial with peristaltic infusion pump |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9% sterile sodium chloride infusion bag | |||
| Sterile tubing intravenous (IV) administration sets (with a clamp to regulate or stop flow) | |||
| 3-way stopcock | Optional | ||
| Disposable syringe fitted with syringe shield and a disposable sterile needle | |||
| Filtered vent needle | Optional | ||
| Syringe pump | Optional | ||
| 2.5-cm, 20-gauge needle (short needle) | |||
| 9-cm, 18-gauge needle (long needle) | |||
| Infusion pump | Optional | ||
| 2.5-cm, 20-gauge needle (short venting needle) | |||
| Peristaltic pump |
Step-by-step
Prior to RLT administration
For all administration methods, the IV catheter should be flushed with ≥10 mL of 0.9% sterile NaCl solution to ensure patency and minimize the risk of extravasation. Any cases of extravasation should be managed according to institutional guidelines.1,2


Expert insight
Syringe method (+/- syringe pump) administration steps1,2
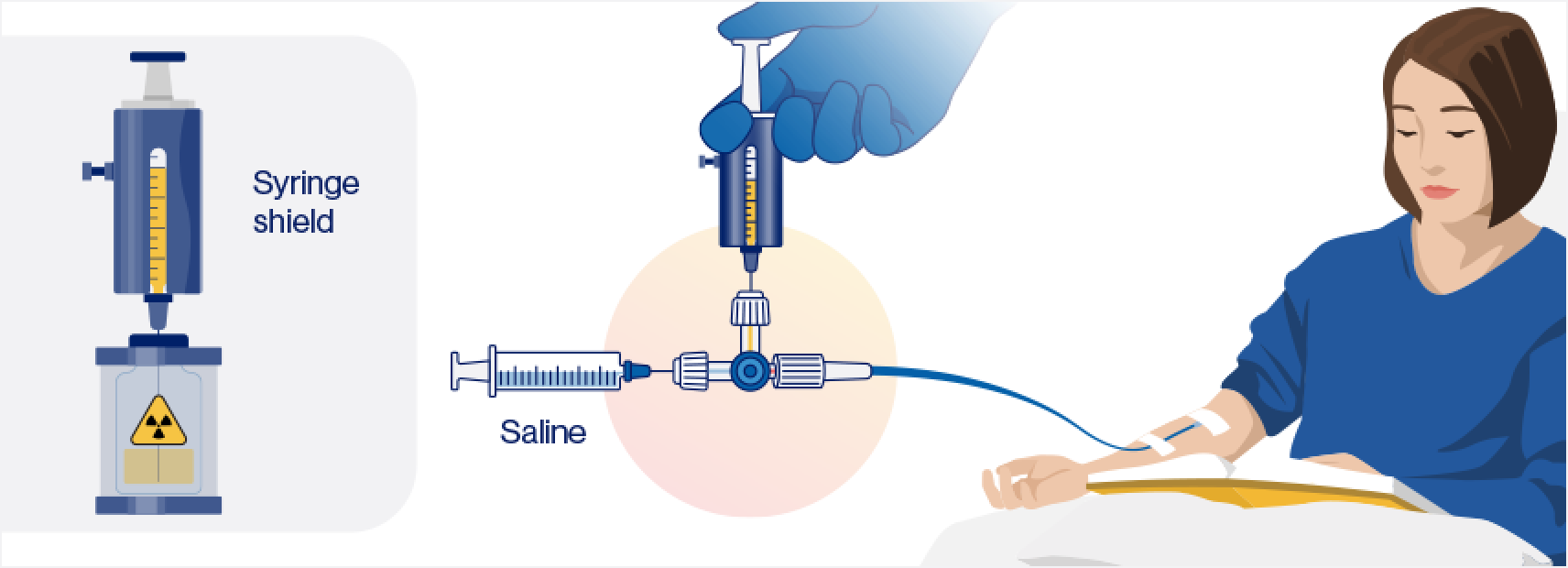
Step 1: Disinfect the vial stopper and withdraw an appropriate volume of RLT solution to deliver the desired radioactivity. Use a disposable syringe fitted with a syringe shield and a disposable sterile needle.
Step 2: Administer the RLT using the prefilled syringe. This can be done via slow IV infusion, either manually or with a syringe pump, through an IV catheter prefilled with 0.9% sterile NaCl solution.
Step 3: After administering the desired radioactivity, flush the IV catheter with 0.9% sterile NaCl solution.
Gravity method (+/- an infusion pump) administration steps1,2
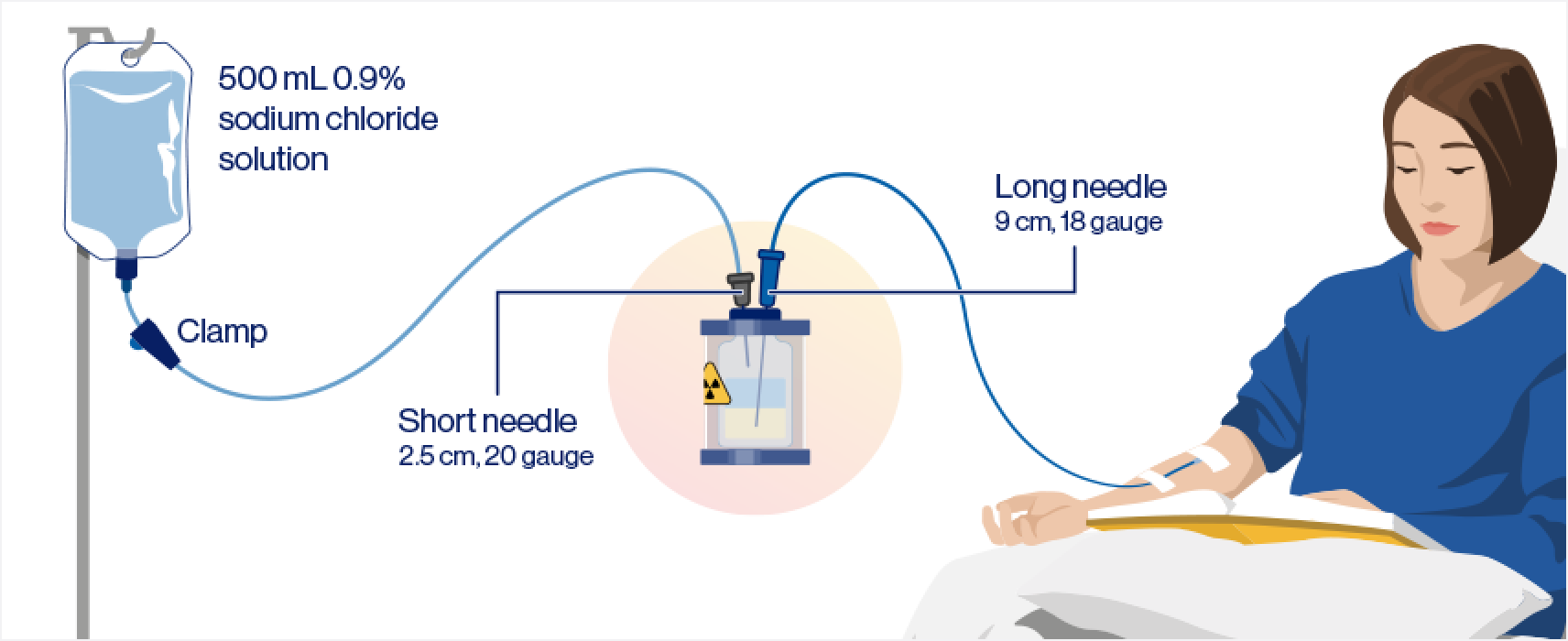
Step 1: Prefill the IV catheter connected to the patient with 0.9% sterile NaCl
Step 2: Infuse sterile 0.9% NaCl solution directly into the vial containing the RLT solution, transporting the RLT solution from the vial to the patient:
- Maintain a constant solution level in the RLT vial
- Ensure the short needle does not touch the solution in the vial
- Do not connect the short needle directly to the patient
- The long needle must touch and rest at the bottom of the vial and remain connected to the patient via an intravenous catheter, prefilled with 0.9% NaCl solution, throughout the infusion
Step 3: Once the desired radioactivity has been administered, perform an IV flush of 0.9% sterile NaCl solution through the IV catheter to the patient


Expert insight
Using the gravity method to administer a reduced dose of RLT is not recommended, as it can lead to the delivery of an incorrect volume of RLT if the dose is not adjusted before administration.
Vial with peristaltic infusion pump administration steps1,2
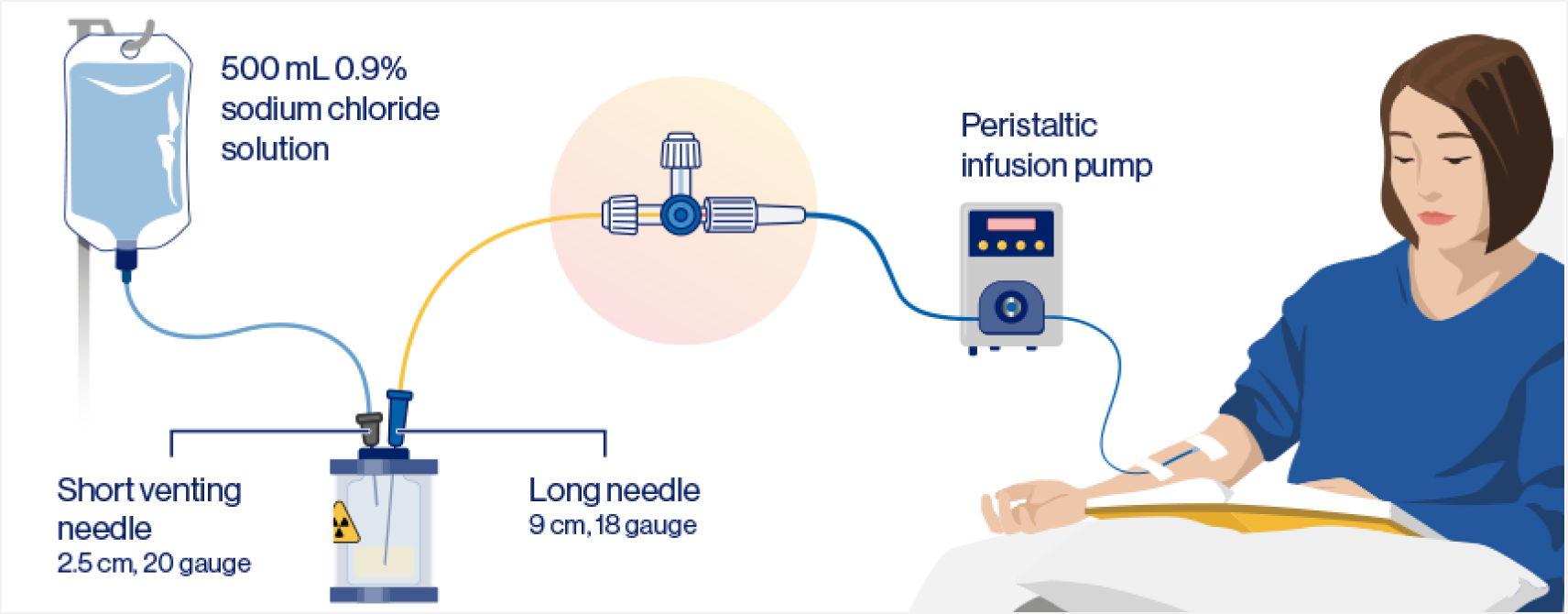
Step 1: Prefill the IV catheter connected to the patient with 0.9% sterile NaCl
- Sterile 0.9% NaCl solution and the RLT vial are connected to the patient via a 3-way stopcock, allowing controlled transport of either sterile 0.9% NaCl solution or the RLT solution into the patient
Step 2: Set the 3-way stopcock so that the RLT solution is in line with the pump, and start the pump to infuse the RLT solution
- Ensure the short needle does not touch the solution in the vial
- Do not connect the short needle directly to the patient or the peristaltic infusion pump
- The long needle must rest at to the bottom of the vial and remain in place for the entire infusion
Step 3: After administering desired radioactivity:
- Stop the peristaltic pump and adjust the position of the stopcock valve so that the pump is aligned with the 0.9% sterile NaCl solution
- Restart the pump to infuse an IV flush of 0.9% sterile NaCl solution
